How Digitalization Is Transforming Oil and Gas Process Management
The oil and gas industry, a behemoth of the global economy, is undergoing a profound transformation. In an era defined by market volatility, increasing environmental scrutiny, and the relentless pursuit of efficiency, digitalization has emerged as a critical enabler of success. This shift from traditional, often manual, processes to a digitally-driven ecosystem is revolutionizing every facet of oil and gas operations, from exploration and production to refining and distribution. By harnessing the power of data, companies are unlocking new levels of productivity, safety, and sustainability, paving the way for a more resilient and profitable future.
This in-depth blog post will explore the multifaceted impact of digitalization on oil and gas process management. We will delve into the key technologies driving this change, examine real-world case studies with quantifiable results, and discuss the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
The Driving Forces Behind Digitalization in Oil and Gas
The impetus for the oil and gas industry’s digital transformation is multifaceted. A confluence of economic, environmental, and technological factors is compelling companies to embrace change and innovate.
Economic Pressures and Market Volatility: The oil and gas market is notoriously cyclical, with fluctuating prices creating a high-pressure environment for operators. In this landscape, the ability to optimize production, reduce operational expenditures (OPEX), and maximize capital efficiency is paramount. Digital technologies offer a powerful toolkit for achieving these goals, enabling data-driven decisions that enhance profitability even in low-price environments.
Heightened Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Scrutiny: The global focus on sustainability and the energy transition is placing increasing pressure on the oil and gas industry to minimize its environmental footprint. Stakeholders, from investors to consumers, are demanding greater transparency and accountability regarding emissions, flaring, and other environmental impacts. Digital solutions provide the means to monitor and manage these factors more effectively, helping companies meet regulatory requirements and enhance their social license to operate.
The Maturation of Digital Technologies: The rapid advancement and increasing affordability of digital technologies have made their adoption more accessible and impactful than ever before. The convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), cloud computing, and blockchain is creating a perfect storm of innovation, offering solutions to some of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
Key Digital Technologies Revolutionizing Process Management
A suite of powerful digital technologies underpins the transformation of oil and gas process management. Each offers unique capabilities that, when integrated, create a synergistic effect, amplifying the benefits across the value chain.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Predictive Maintenance
The Internet of Things (IoT) forms the bedrock of the digital oilfield. A vast network of sensors and connected devices deployed across assets—from downhole pumps to pipeline valves—collects real-time data on a massive scale. This continuous stream of information provides unprecedented visibility into operational performance and asset health.
One of the most impactful applications of IoT is predictive maintenance. By analyzing data on parameters like vibration, temperature, and pressure, AI-powered algorithms can predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows companies to move away from reactive, and often costly, maintenance schedules.
A prime example of this is the implementation of IoT for predictive maintenance on offshore platforms. The ability to anticipate equipment malfunctions prevents costly unplanned downtime, which can run into millions of dollars per day. Furthermore, it enhances safety by reducing the need for personnel to work in hazardous environments.
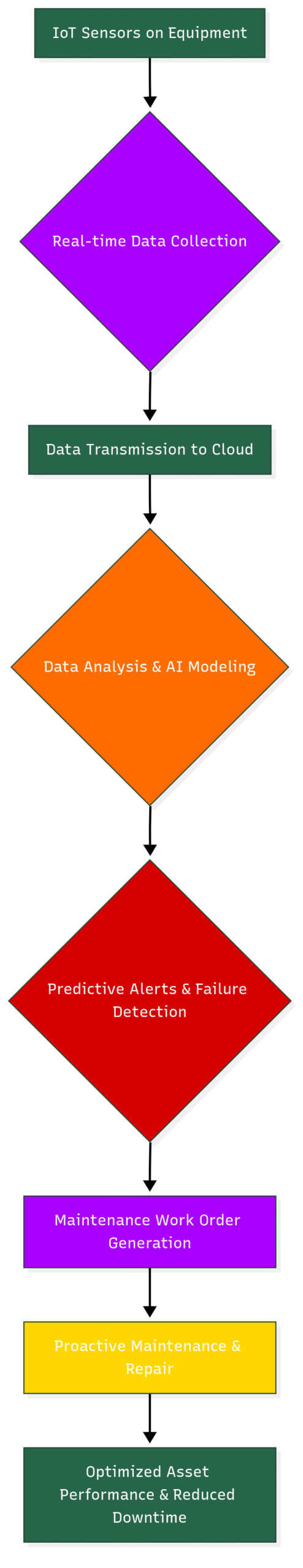
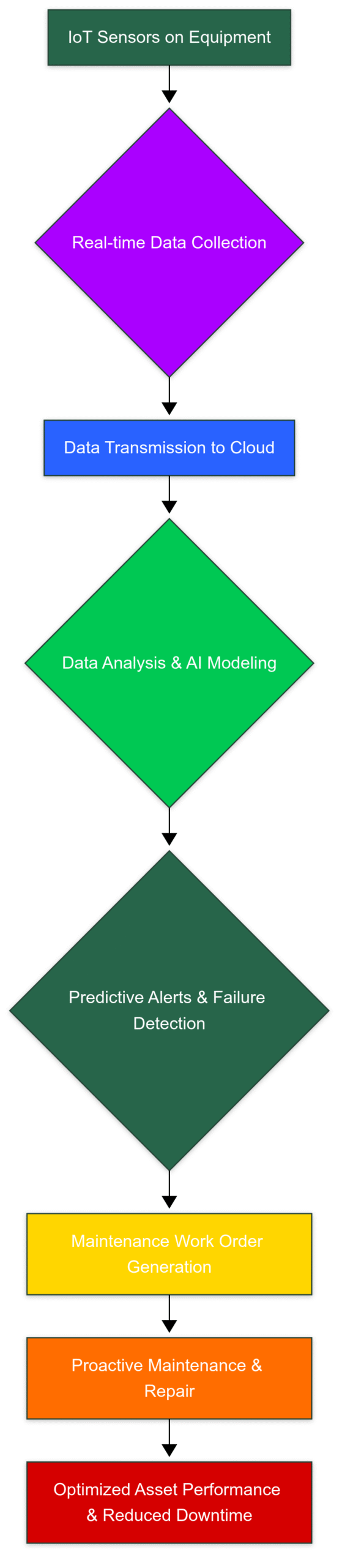
Mermaid Block Diagram: The Predictive Maintenance Process
This diagram illustrates the flow of data from IoT sensors to the cloud for analysis, leading to predictive alerts and proactive maintenance, ultimately optimizing asset performance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) for Enhanced Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are the brains behind the digital transformation, turning raw data into actionable insights. In the oil and gas industry, their applications are vast and varied, touching every stage of the process.
Upstream Operations: In exploration and production, AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of seismic and geological information to identify promising drilling locations with greater accuracy. This significantly reduces exploration risks and costs. For instance, AI can analyze subsurface data to create detailed reservoir models, enabling engineers to optimize drilling paths and maximize hydrocarbon recovery. Companies like Shell and ExxonMobil have reported significant reductions in drilling time and costs by leveraging AI in their exploration activities.
Midstream and Downstream Operations: In the transportation and refining sectors, AI and ML optimize logistics, improve process efficiency, and enhance safety. AI can be used to optimize pipeline scheduling, minimizing bottlenecks and reducing transportation costs. In refineries, ML models can analyze real-time process data to optimize yields and energy consumption, leading to significant cost savings and reduced emissions.
Digital Twins: A Virtual Mirror of Physical Assets
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system. This dynamic model is continuously updated with real-time data from IoT sensors, creating a living, breathing digital counterpart to the physical world. Digital twins provide a powerful platform for simulation, analysis, and optimization.
In the context of an offshore oil platform, a digital twin can be used to:
Simulate different operational scenarios to identify the most efficient production strategies.
Conduct virtual stress tests to assess the structural integrity of the platform under various weather conditions.
Train operators in a safe and controlled virtual environment.
Plan and de-risk complex maintenance activities before they are performed in the physical world.
The implementation of digital twins has been shown to significantly reduce operational costs, improve safety, and extend the lifespan of assets.
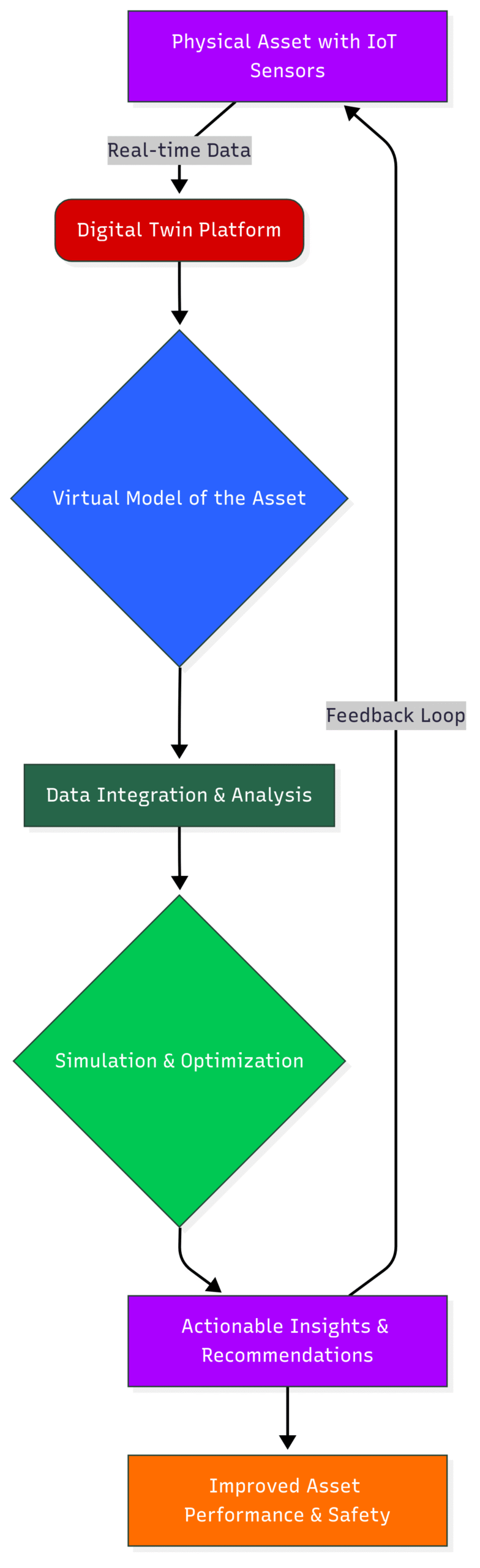
Mermaid Block Diagram: The Digital Twin Workflow
This diagram showcases the continuous flow of data from a physical asset to its digital twin, enabling simulation, optimization, and a feedback loop for improved performance.
Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency and Security in the Supply Chain
The oil and gas supply chain is a complex web of transactions and interactions involving multiple stakeholders. This complexity can lead to inefficiencies, disputes, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable ledger, offers a powerful solution to these challenges.
By creating a single, shared source of truth for all transactions, blockchain can:
Streamline and automate trade finance processes, reducing paperwork and transaction times.
Improve the traceability of hydrocarbons from the wellhead to the end consumer, combating fraud and ensuring product quality.
Enhance the security and transparency of joint venture agreements and other contractual arrangements.
Facilitate the tracking of carbon emissions throughout the value chain, supporting ESG reporting and sustainability initiatives.
Mermaid Block Diagram: Blockchain-Enabled Oil and Gas Supply Chain
This diagram illustrates how blockchain provides end-to-end traceability and automates processes across the oil and gas supply chain, enhancing security and efficiency.
Real-World Success Stories: The Tangible Benefits of Digitalization
The theoretical benefits of digitalization are compelling, but it is the real-world success stories that truly demonstrate its transformative power. Here are a few examples of how oil and gas companies are leveraging digital technologies to achieve impressive results:
Shell’s Predictive Maintenance Program: Shell has implemented a comprehensive predictive maintenance program across its global assets, leveraging IoT and AI to monitor equipment health. This has resulted in a significant reduction in unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. In some cases, they have reported a 10-15% reduction in maintenance costs and a 20% decrease in unscheduled downtime.
ADNOC’s Panorama Digital Command Centre: The Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) has established a state-of-the-art digital command center that provides real-time visibility into its entire value chain. This has enabled the company to optimize production, reduce costs, and improve decision-making. ADNOC has reported billions of dollars in value creation through this initiative.
BP’s Use of Digital Twins: BP has been a pioneer in the use of digital twins for its offshore platforms. By creating virtual replicas of its assets, the company has been able to optimize production, improve safety, and reduce the need for costly and hazardous offshore inspections. They have seen production increases of up to 5% in some fields through the use of digital twin technology.
Navigating the Challenges of Digital Transformation
Despite the immense potential of digitalization, the journey is not without its challenges. Oil and gas companies must navigate a number of hurdles to successfully implement and scale their digital initiatives.
Legacy Systems and Infrastructure: The industry is characterized by a significant amount of aging infrastructure and legacy IT systems. Integrating new digital technologies with these existing systems can be complex and costly.
Data Management and Cybersecurity: The proliferation of IoT devices and digital technologies generates vast amounts of data. Managing, storing, and securing this data is a significant challenge. The interconnected nature of digital systems also increases the risk of cyberattacks, making robust cybersecurity measures essential.
Organizational Culture and Change Management: Perhaps the biggest challenge is the cultural shift required to embrace digitalization. A successful transformation requires a change in mindset, a willingness to adopt new ways of working, and strong leadership to drive the change. Overcoming resistance to change and upskilling the workforce are critical for success.
Scalability and Interoperability: Proving the value of a digital solution in a pilot project is one thing; scaling it across a global organization is another. Ensuring that different digital systems can communicate and work together seamlessly (interoperability) is a key technical challenge.
The Future of Digitalization in Oil and Gas: A Glimpse into Tomorrow
The digital transformation of the oil and gas industry is still in its early stages, and the future holds even greater promise. Several key trends are shaping the next wave of innovation:
The Rise of the Autonomous Oilfield: The concept of a fully autonomous oilfield, where operations are managed and optimized by AI with minimal human intervention, is becoming increasingly plausible. This will be enabled by further advancements in robotics, AI, and edge computing.
Increased Focus on Sustainability and the Energy Transition: Digital technologies will play a crucial role in helping the oil and gas industry navigate the energy transition. This includes using AI to optimize carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects, leveraging blockchain to track and trade carbon credits, and using digital twins to design and operate more energy-efficient facilities.
The Proliferation of Edge Computing: As the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow, there will be a greater need to process this data at the “edge” of the network, closer to the source. Edge computing will enable faster decision-making and reduce the strain on centralized cloud infrastructure.
Hyper-automation and the Intelligent Enterprise: The future will see a move towards hyper-automation, where AI and machine learning are used to automate increasingly complex tasks and processes. This will lead to the creation of the “intelligent enterprise,” where data-driven insights are embedded in every aspect of the organization.
Conclusion: Embracing the Digital Imperative
Digitalization is no longer a choice for the oil and gas industry; it is an imperative. The companies that successfully embrace this transformation will be the ones that thrive in the years to come. By leveraging the power of IoT, AI, digital twins, and blockchain, oil and gas companies can unlock new levels of efficiency, safety, and sustainability. The journey is not without its challenges, but the rewards—a more resilient, profitable, and sustainable future—are well worth the effort. The digital revolution in the oil and gas industry has begun, and its impact will be felt for generations to come.