Recent Updates
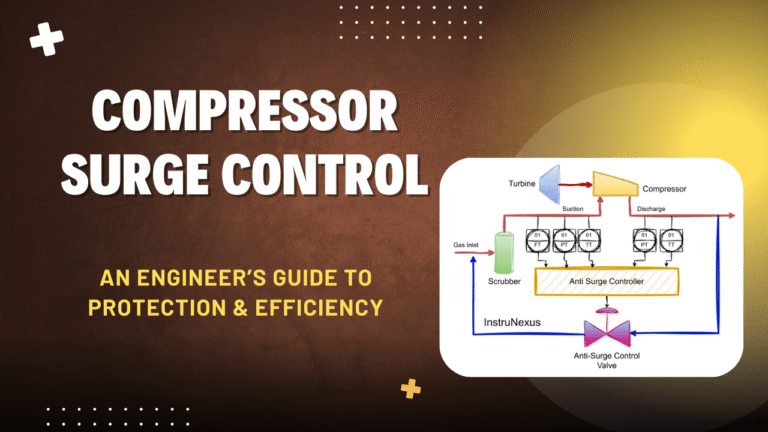
Interactive Guide to Compressor Anti-Surge Control Anti-Surge Control The Problem The Solution Providers Load Sharing Engineer’s Toolkit Protecting the Heart of Industry An interactive exploration of compressor anti-surge control systems. Discover the dynamics of aerodynamic surge, the sophisticated technologies designed to prevent it, and the critical knowledge required to ensure...
Onshore vs. Offshore Instrumentation Design: An Interactive Comparison Onshore vs. Offshore Overview Environment Design & Execution Cabling Components Safety Lifecycle OverviewEnvironmentDesign & ExecutionCablingComponentsSafetyLifecycle A Tale of Two Environments An interactive comparison of Onshore and Offshore instrumentation design, exploring how environment dictates two fundamentally different engineering philosophies. Comparative Complexity Overview This...
Interactive Fault Tree Analysis Explorer Fault Tree Analysis Explorer Fundamentals Methodology Analysis Tools Case Studies Deconstructing Failure, Engineering Safety. Welcome to the Interactive Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) Explorer. This application translates the comprehensive principles of FTA into a dynamic, explorable experience. Discover the core concepts, methodologies, and real-world applications of...
Interactive Guide to the Purdue Model (PERA) The PERA Interactive Guide …Introduction… The Model… Security Doctrine… Threats & Cases… Standards & Future… From Factory Blueprint to Cyber Fortress Explore the Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA), the accidental standard that became the foundational doctrine for defending the world’s most critical industrial...
Interactive Guide to Radar Level Measurement Radar Level Guide Principles Technology Modulation Application Installation Full Report An Interactive Guide to Radar Level Measurement Explore the principles, technologies, and applications of modern radar level transmitters. This guide translates complex technical data into an interactive experience to help you understand and select...
Pressure Pressure &DP Transmitters Flow Orifice PlateMagnetic FlowmeterVortex flowmeterCoriolis FlowmeterUltrasonic FlowmeterRotameter.xlsxPositive DisplacementThermal mass flowmeter Temperature Temperature ElementsTemperature Transmitter Pressure & Temperature Gauge Level Displacer Level TransmitterGuided Wave Radar Level TransmitterFloat and Tape Level TransmitterUltrasonic Level Transmitter Valves ESD valveControl Valve Control System System Cabinets (DCS/IPS/F&G) Integrated Control and Safety System (ICSS)...
Interactive Report: Process Analyzers in LNG Facilities Process Analyzers in Modern LNG Facilities An interactive guide to the critical analytical instrumentation in LNG production. Explore the LNG Process Train The journey of natural gas through an LNG plant is a continuous process of purification and cooling. Click on any stage...
Comprehensive Refinery Process Analyzer Guide Refinery Process Analyzers Overview Refinery Flow Technologies Implementation Future Trends The Strategic Role of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) This application provides an interactive guide to the process analyzers used in modern petroleum refining. Process analyzers are the real-time sensory organs of a refinery, enabling a...
Universal Instrument Datasheet — Final Self-Verification Checklist Universal Instrument Datasheet — Final Self-Verification Checklist Applies to pressure/temperature/flow/level transmitters; control & shutdown valves; basic analyzers. Expand all Collapse all Check all Uncheck all Save Load Reset Print / PDF 0 of 0 checked Header & Document Control Document number & title...